How Many Types Of Cabling Are Used In Data Centers?
How Many Types Of Cabling Are Used In Data Centers?
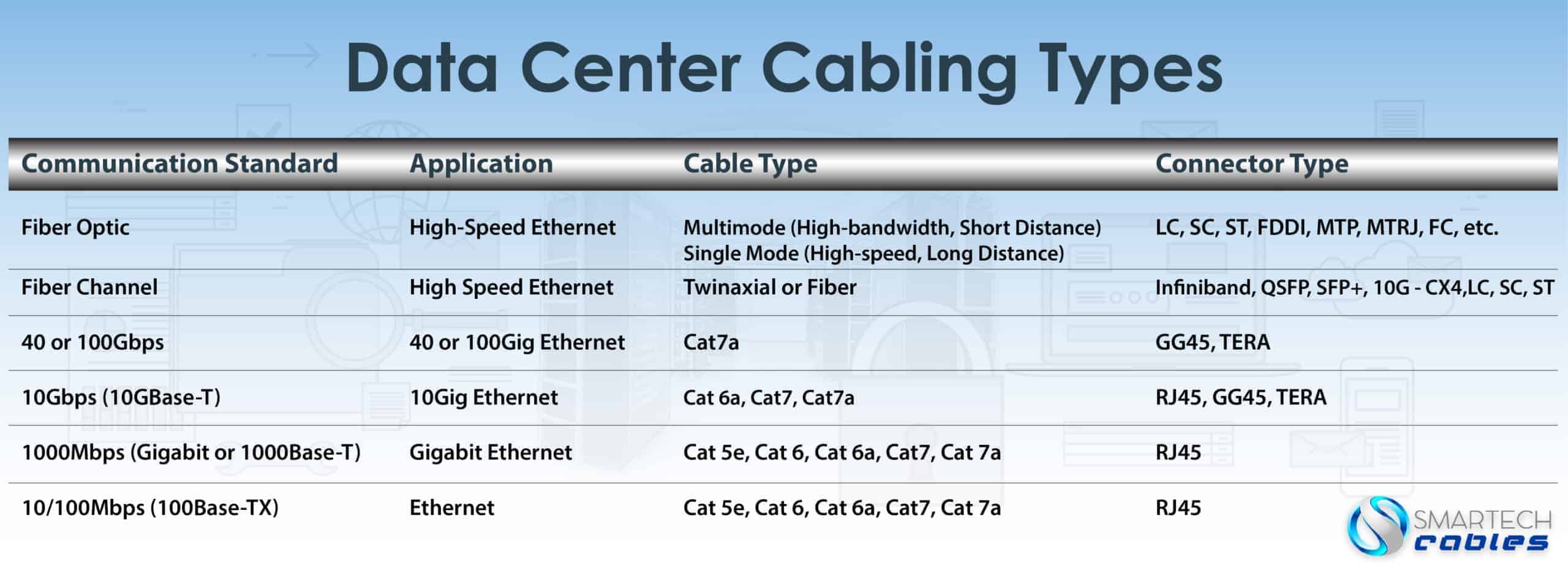
Data centers are a centralized place of any infrastructure or building containing computing solutions and networks used for collecting, processing, and distribution of data. Cables are an integral part of any network. Data centers use various types of cables; pure copper ethernet cables, fiber optics, AC/DC power, and ground are some of them. Now, the big question is how do you determine which cable kind of cable to use? There are many factors involve in determining the best cable type for a data center. Analyzing the interface of equipment used in data centers and bandwidth requirements are some of those factors. We'll discuss copper cables and fiber optics in this article. But before we get on to that, first you need to know about the cabling process in data centers.
Cabling Process in Data Centers:
There are two ways for the cabling process in data centers: structured and unstructured. Structured cabling is more of a predefined standard-based design in which pathways and connection points are also predefined. Furthermore, it is tested to guarantee proper performance. The structured design has well ordered and categorized cables. The installation of a structured design takes more time and money because it is all organized and systemic. But the operational cost of this design is low and it is durable for long runs as compared to unstructured design.
In unstructured cabling design, there are no predefined standards, connection points, or pathways. It is done from point to point. There can be cooling issues in this design because of the restricted airflow. The energy cost can be higher with this design. The management of this design can be really difficult because there is no plan to change cable locations. The lifecycle of this design is short. Now the installation cost is low for unstructured cabling design but the operational cost is very high for this kind of system.
Best Cable for Data Centers: Copper or Fiber?
Organizations use both copper cables and fiber optics to improve data center deployment. In this article, you’ll get to know about both of these cables and their unique features.
Copper Cables:
Now copper cable might not be as good as fiber optics but it certainly has its benefits. Fiber optic cables do not face electromagnetic interference issues because they emit photons and that is why signals from these cables can travel at a longer distance. There is no doubt that fiber optics provide faster communications but we cannot replace copper cables entirely with them. Copper cables have a low cost and it increases performance.
Cable Distance:
Copper cables cover a distance of several meters. The ranging of the cables generally depends on the speed of the network. However, this cable is enough to cover all the connections inside the data center. Copper cables have the capability of transmitting data at the highest bandwidth. These cables offer connections consistently and reasonably.
Another good feature of copper cable is that they are cost-efficient as compared to fiber optics. These cables are somewhat 2 to 5 times less costly than active cables. Power saving is another cool feature that copper cable comes with. Due to its thermal design, it needs less amount of power for cooling. Data centers can save a lot of energy by using these cables.
Guaranteed Best Price !
Consistency:
Reliability and consistency are some of the major benefits that come with copper cables. The reliability is measured in MTBF (mean time between failure) which is fifty million for these cables. This number is much higher in fiber optic cables. Organizations that don't want the downtime of their data center should go for these copper cables.
Fiber Optics:
That is enough for copper cables. Now let’s move on to the fiber optic cables:
Fiber Optic Range:
The copper cables provide connections between the equipment that is placed in a single rack. The range of the copper cable is between 7 to 10 meters.
Fiber optic cables have electronics and optics in the connectors instead of wires in them. This feature allows the fiber optic to cover more distance. The connectors at both ends of the cable convert the electrical signals to optical signals and another way around. This active fiber optic cable is equally good for both intra-and inter-rack applications.
Characteristics:
The fiber optic has the same data rate as copper cable but it is lighter and thinner than copper cable. The fiber optic does not have any shielding which makes them less bulky than the copper cables. Its bend radius is also smaller. All these features give more flexibility for data center configuration.
They Make a Good Couple:
There are a few data centers that use only one type of cable for their systems. The ideal situation would be to use these two cables together. Fiber optic provides more flexibility and copper cable cuts down the cost. So, the best approach would be to use these cables together based on the networking requirements.